Steam Valves
ARI CHECKO-V Lift Check Valve (Flanged PN40, Cast Steel Body)
ARI CHECKO-V Lift Check Valve (Flanged PN40, Cast Steel Body)
Couldn't load pickup availability
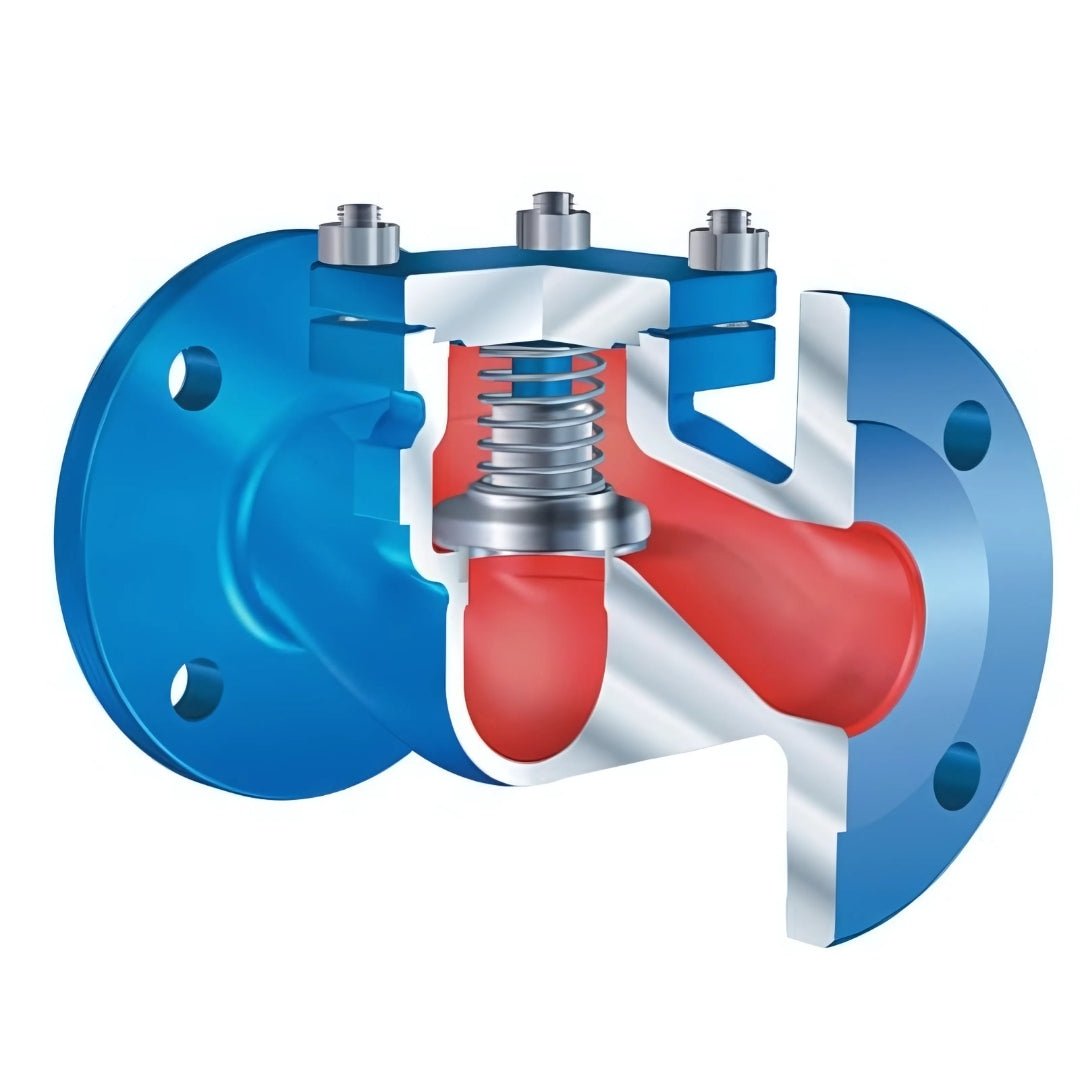
The ARI CHECKO-V Lift Check Valve with PN40 flanged ends and a cast steel body is a high-performance non-return valve designed to prevent reverse flow in steam, gas, and liquid pipelines. Its vertical lift mechanism allows flow in one direction while automatically closing when reverse pressure is detected, safeguarding equipment such as pumps, compressors, and control valves.
Built with a durable cast steel body, this valve offers excellent strength, thermal resistance, and long-term reliability — even in demanding process environments. The PN40 pressure rating ensures safe and consistent operation in high-pressure applications, making it suitable for steam systems, power plants, chemical processing, and industrial utilities. The flanged connections allow secure installation, easy maintenance access, and full compatibility with standard pipeline systems.
Designed and manufactured by ARI Armaturen, the CHECKO-V combines German engineering precision with robust functionality, making it a trusted choice where performance and protection are critical.
Key Features
Cast Steel Construction
Strong and heat-resistant body ideal for high-temperature, high-pressure service conditions.
PN40 Flanged Ends
Engineered for safe installation into high-pressure pipeline systems up to 40 bar.
Lift-Type Check Mechanism
Automatically closes against reverse flow to protect downstream equipment.
Compact, In-Line Design
Optimised for vertical or horizontal mounting with minimal space requirements.
Maintenance-Friendly
Flanged design allows for quick inspection and servicing of internal components.
Reliable Non-Return Protection
Essential in steam, gas, and liquid applications across industrial and energy sectors.
Share
FAQ's
What is the difference between a valve and an actuator?
What types of actuators are available?
The main types of actuators are:
Pneumatic actuators – use compressed air for fast, reliable operation.
Electric actuators – use electrical power for precise control.
Hydraulic actuators – use fluid pressure for high-torque applications.
Each type offers unique advantages depending on the environment, media, and system control needs.
How do I choose the right actuator for my valve?
To select the correct actuator, consider:
Valve type and torque requirement
Power source available (air, electric, or hydraulic)
Operating environment (temperature, humidity, hazardous area)
Control signal type (on/off or modulating)
Matching actuator torque and compatibility with the valve’s ISO mounting ensures reliable performance.
What are the main types of valves used in automation?
The most common valves in automated systems include:
Ball valves – for tight shutoff and quick operation.
Butterfly valves – for larger flow control with compact design.
Globe valves – for precise throttling and flow regulation.
Check valves – to prevent backflow.
Gate valves – for full bore flow isolation.
What’s the difference between a double-acting and spring-return actuator?
Double-acting actuators use air (or power) to both open and close the valve.
Spring-return actuators use air to open (or close) the valve, and a built-in spring to automatically return it to a safe position when power or air is lost — ideal for fail-safe operation.
How often should valves and actuators be serviced?
Regular maintenance intervals depend on operating conditions, but a good rule of thumb is to inspect every 6–12 months.
This includes checking for leaks, lubrication, seal wear, and actuator responsiveness to prevent unexpected downtime.

