Steam Valves
Ari Armaturen FABA+ ANSI Bellows Sealed Globe Valve (Flanged ANSI 150, Cast Steel Body)
Ari Armaturen FABA+ ANSI Bellows Sealed Globe Valve (Flanged ANSI 150, Cast Steel Body)
Couldn't load pickup availability
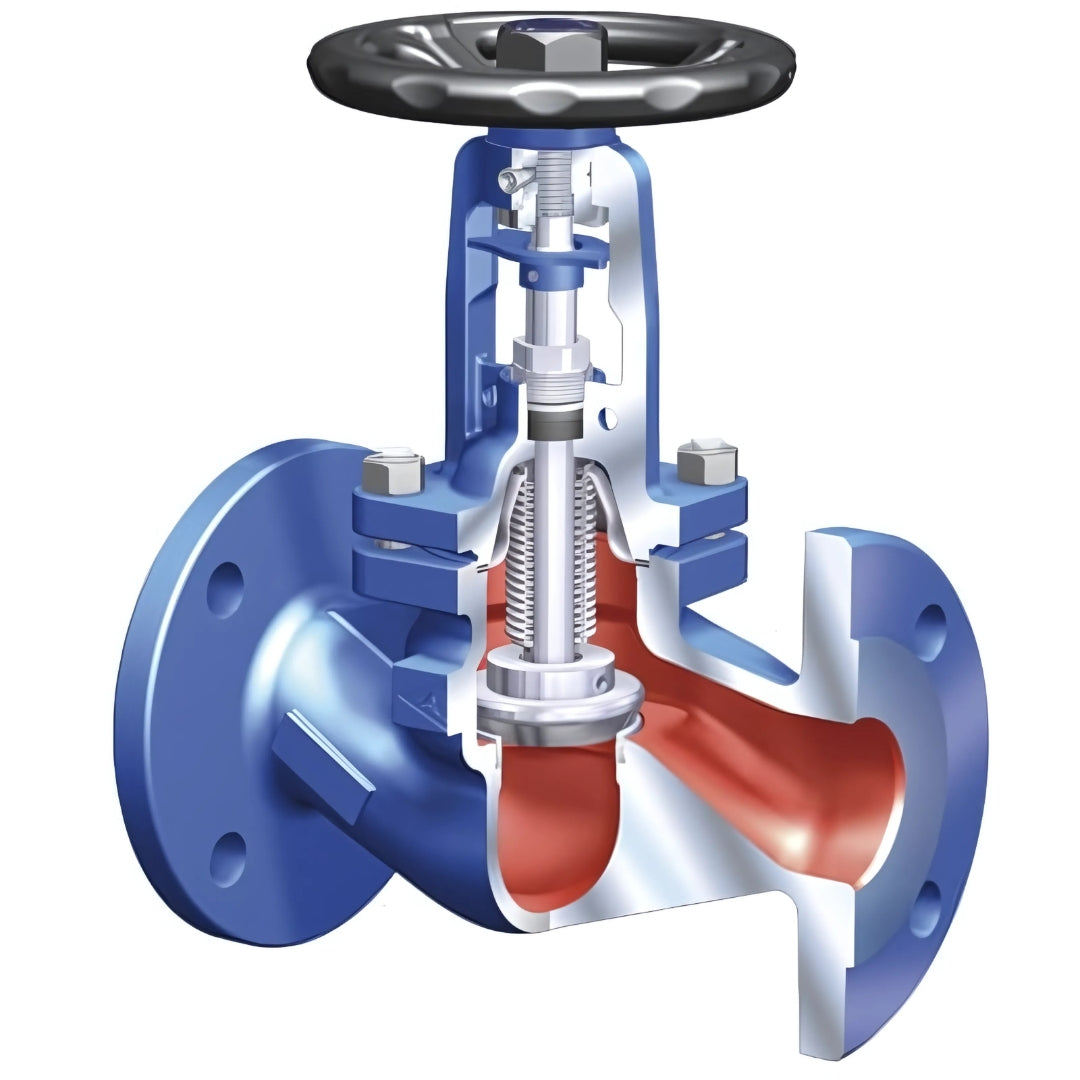
The Ari Armaturen FABA+ ANSI Bellows Sealed Globe Valve with ANSI 150 flanged ends and a cast steel body is engineered for reliable shut-off and flow control in process systems where leak-tight performance is critical. Designed to prevent fugitive emissions, this valve uses a high-integrity bellows seal to eliminate stem leakage — making it ideal for use with steam, thermal oil, and hazardous process media.
Constructed from robust cast steel, the valve body offers excellent mechanical strength and resistance to high temperatures, pressure fluctuations, and aggressive conditions. The ANSI 150 flange rating ensures full compatibility with standard North American piping systems operating at moderate pressures. Its bellows seal system, combined with a rising stem and backseat feature, delivers double stem sealing for enhanced operational safety and extended service life.
Trusted across industries such as power generation, petrochemical refining, and industrial steam systems, the ARI FABA+ Bellows Sealed Globe Valve is known for its precise flow control, long-term durability, and compliance with emission reduction standards.
Key Features
Bellows Sealed Construction
Provides zero stem leakage by sealing the stem with a stainless steel multi-layer bellows — ideal for toxic or high-temp applications.
Cast Steel Body
Rugged, thermally stable construction suitable for steam, condensate, oil, and process fluid systems.
ANSI 150 Flanged Ends
Fully compatible with Class 150 pipelines, allowing easy integration into American-standard piping networks.
Backseat Design
Secondary sealing when the valve is fully open, increasing operational safety and service flexibility.
Accurate Globe Valve Control
Provides linear flow characteristics for precise modulation and shut-off.
Maintenance-Friendly Layout
Top-entry design with easily serviceable internals for reduced downtime and lifecycle costs.
Share
FAQ's
What is the difference between a valve and an actuator?
What types of actuators are available?
The main types of actuators are:
Pneumatic actuators – use compressed air for fast, reliable operation.
Electric actuators – use electrical power for precise control.
Hydraulic actuators – use fluid pressure for high-torque applications.
Each type offers unique advantages depending on the environment, media, and system control needs.
How do I choose the right actuator for my valve?
To select the correct actuator, consider:
Valve type and torque requirement
Power source available (air, electric, or hydraulic)
Operating environment (temperature, humidity, hazardous area)
Control signal type (on/off or modulating)
Matching actuator torque and compatibility with the valve’s ISO mounting ensures reliable performance.
What are the main types of valves used in automation?
The most common valves in automated systems include:
Ball valves – for tight shutoff and quick operation.
Butterfly valves – for larger flow control with compact design.
Globe valves – for precise throttling and flow regulation.
Check valves – to prevent backflow.
Gate valves – for full bore flow isolation.
What’s the difference between a double-acting and spring-return actuator?
Double-acting actuators use air (or power) to both open and close the valve.
Spring-return actuators use air to open (or close) the valve, and a built-in spring to automatically return it to a safe position when power or air is lost — ideal for fail-safe operation.
How often should valves and actuators be serviced?
Regular maintenance intervals depend on operating conditions, but a good rule of thumb is to inspect every 6–12 months.
This includes checking for leaks, lubrication, seal wear, and actuator responsiveness to prevent unexpected downtime.

