Valves UK
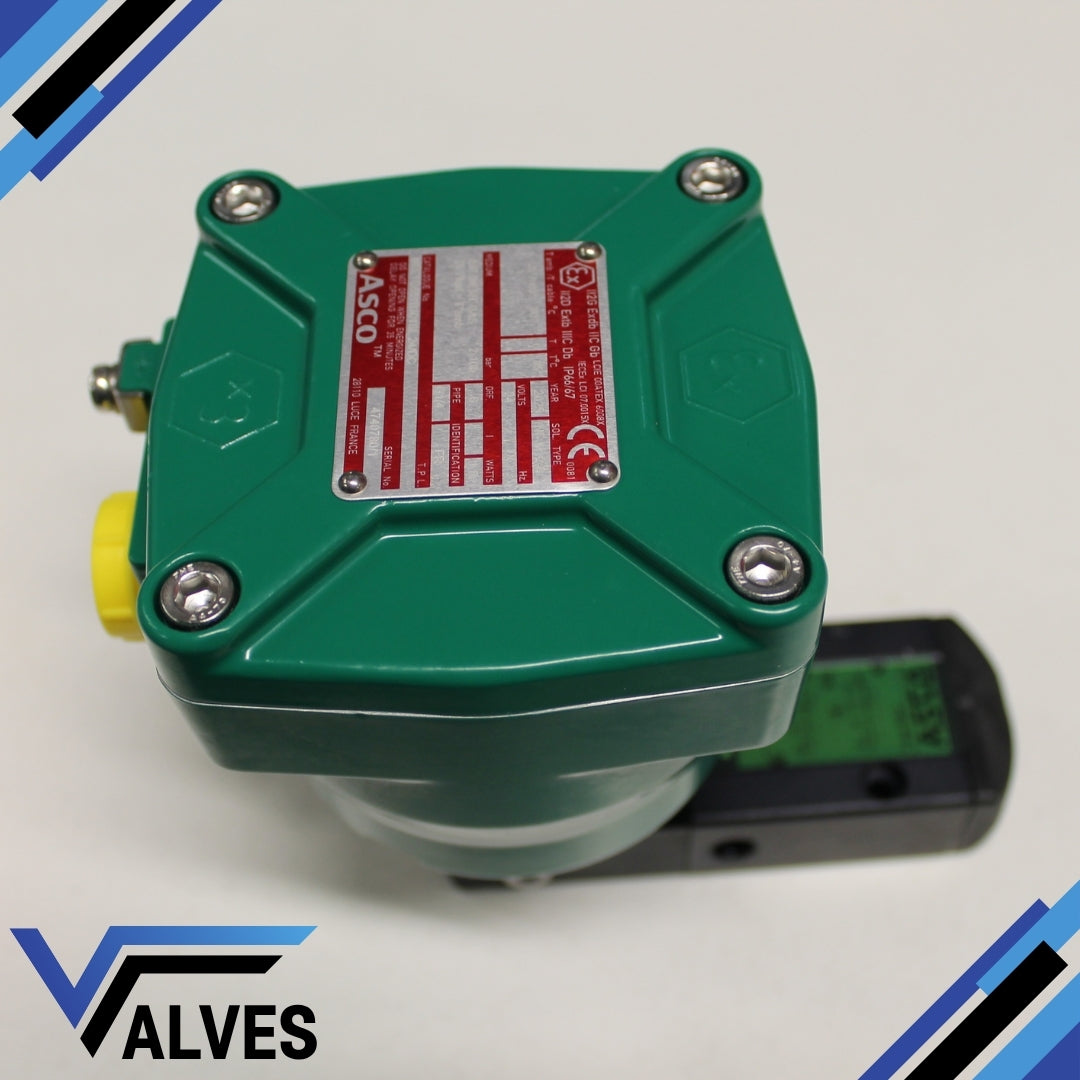
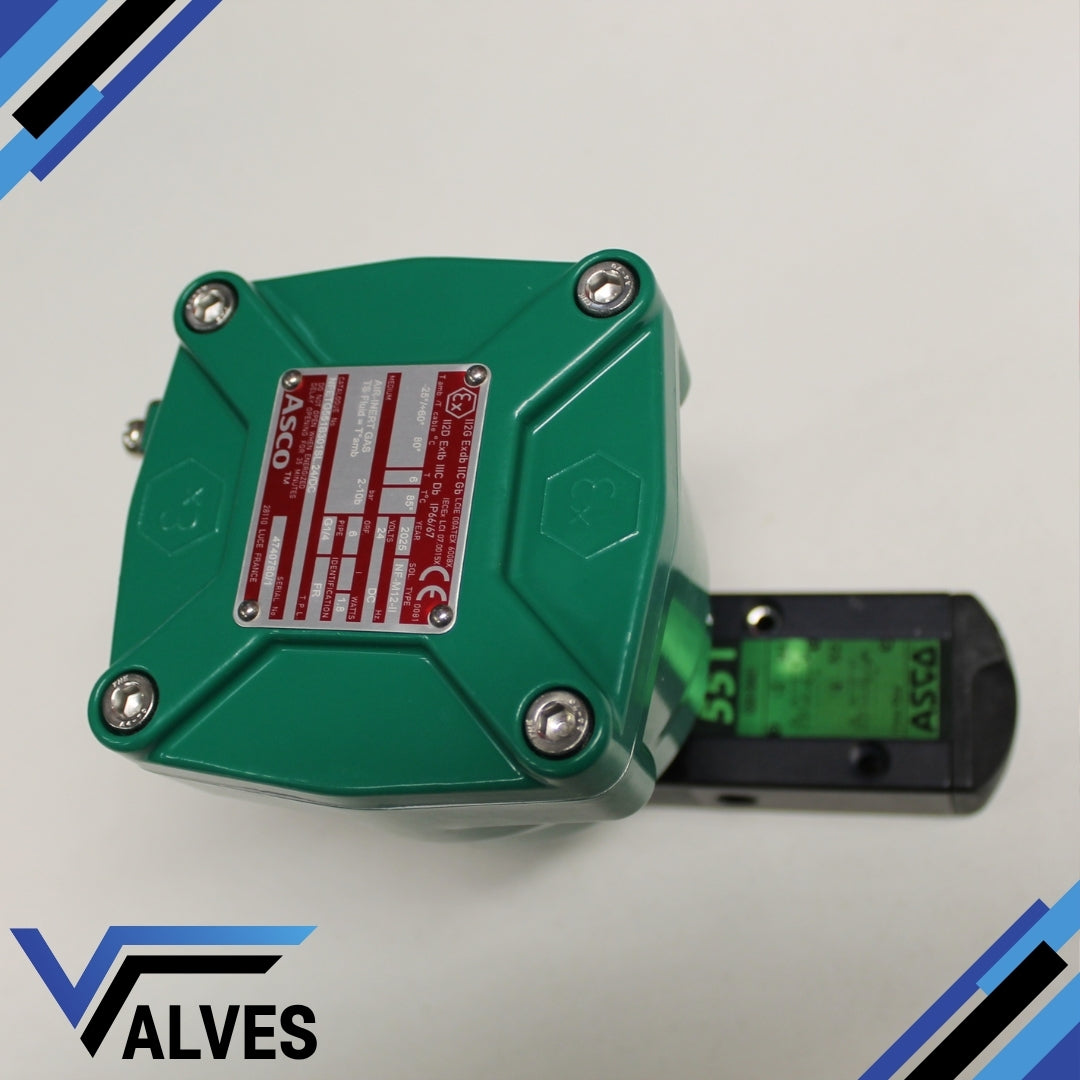
ASCO NFETG551B301SL.24/DC Numatics Pilot Operated Solenoid Valve
ASCO NFETG551B301SL.24/DC Numatics Pilot Operated Solenoid Valve
Couldn't load pickup availability
IN STOCK - SAME DAY DISPATCH
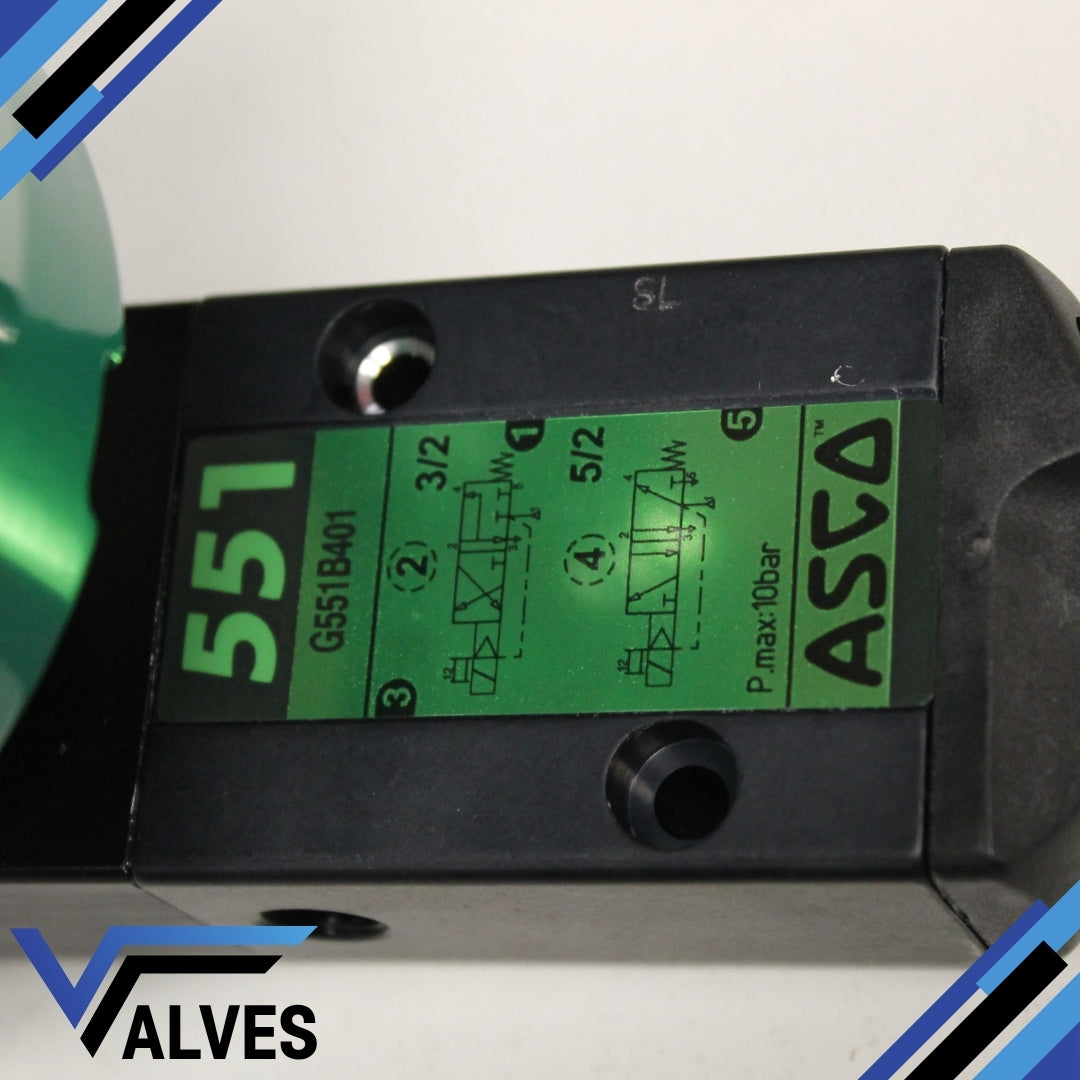
The ASCO NFETG551B301SL.24/DC Numatics Pilot Operated Solenoid Valve is a compact, high-performance pneumatic valve designed for precision control in industrial automation and process applications. This 3/2–5/2 monostable valve provides dependable operation for both single and double-acting actuators, offering excellent reliability in demanding environments. Constructed from lightweight aluminium with LT-NBR resilient seals, it ensures long service life and resistance to wear under continuous operation.
Key Features:
-
3/2–5/2 pilot operated solenoid valve with manual operator
-
Port size: 1/4" (DN8) G (ISO 228/1)
-
Orifice: 6.0 mm
-
Monostable aluminium body for lightweight durability
-
LT-NBR resilient seals for long-term reliability
-
Coil class: F (1.8 W power consumption)
-
Explosion-proof certified: II2G Ex db IIC Gb / II2D Ex tb IIIC Db T6
-
Protection rating: IP66/67
-
Medium: Air or inert gas
Share




FAQ's
What is the difference between a valve and an actuator?
What types of actuators are available?
The main types of actuators are:
Pneumatic actuators – use compressed air for fast, reliable operation.
Electric actuators – use electrical power for precise control.
Hydraulic actuators – use fluid pressure for high-torque applications.
Each type offers unique advantages depending on the environment, media, and system control needs.
How do I choose the right actuator for my valve?
To select the correct actuator, consider:
Valve type and torque requirement
Power source available (air, electric, or hydraulic)
Operating environment (temperature, humidity, hazardous area)
Control signal type (on/off or modulating)
Matching actuator torque and compatibility with the valve’s ISO mounting ensures reliable performance.
What are the main types of valves used in automation?
The most common valves in automated systems include:
Ball valves – for tight shutoff and quick operation.
Butterfly valves – for larger flow control with compact design.
Globe valves – for precise throttling and flow regulation.
Check valves – to prevent backflow.
Gate valves – for full bore flow isolation.
What’s the difference between a double-acting and spring-return actuator?
Double-acting actuators use air (or power) to both open and close the valve.
Spring-return actuators use air to open (or close) the valve, and a built-in spring to automatically return it to a safe position when power or air is lost — ideal for fail-safe operation.
How often should valves and actuators be serviced?
Regular maintenance intervals depend on operating conditions, but a good rule of thumb is to inspect every 6–12 months.
This includes checking for leaks, lubrication, seal wear, and actuator responsiveness to prevent unexpected downtime.






